Introduction to Break-Even Rate
Understanding your personal break-even rate is essential for navigating
the complexities of personal finance and career decisions. Your
break-even rate represents the hourly wage you must earn to cover all
your expenses and financial obligations. By knowing this crucial figure,
you gain valuable insight into the minimum income needed to maintain
your current lifestyle and financial stability. Whether you’re
considering a job offer, evaluating your budget, or planning for the
future, knowing your break-even rate empowers you to make informed
decisions that align with your financial goals.
Understanding your break-even rate offers numerous benefits that can positively impact your financial well-being and decision-making process. By knowing this critical figure, you gain clarity on your financial situation and can make informed choices about your career, budget, and future plans. Here are some key benefits:
- Financial Clarity: Knowing your break-even rate provides clarity on your minimum income needs to cover expenses.
- Informed Career Decisions: Understanding your break-even rate helps you evaluate job offers and negotiate salaries effectively.
- Budgeting Guidance: Your break-even rate serves as a benchmark for budgeting and financial planning.
- Goal Setting: Knowing your financial baseline enables you to set realistic savings and income goals.
- Confidence in Financial Decisions: Armed with knowledge of your break-even rate, you can make confident financial decisions aligned with your long-term objectives.
- Improved Financial Management: Awareness of your break-even rate fosters better money management habits and encourages proactive financial planning.
- Long-Term Financial Stability: By staying mindful of your break-even rate, you can work towards achieving and maintaining long-term financial stability.
These benefits underscore the importance of knowing and regularly reassessing your break-even rate to support your financial health and goals.
Factors Influencing Break-Even Rate:
Several factors influence your break-even rate, reflecting the complexity of personal finances and individual circumstances. Understanding these factors can help you grasp the dynamics of your financial situation and make informed decisions. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Monthly Expenses: The total amount you spend each month on necessities, such as housing, utilities, groceries, transportation, and healthcare, directly impacts your break-even rate.
- Debt Obligations: The presence of debts, including mortgages, student loans, credit card balances, and other liabilities, affects your break-even rate by increasing your monthly financial obligations.
- Lifestyle Choices: Your lifestyle preferences and discretionary spending habits, such as dining out, entertainment, travel, and leisure activities, can influence your break-even rate by altering your monthly expenses.
- Savings Goals: Your savings objectives, including emergency funds, retirement savings, investment goals, and other financial targets, play a role in determining your break-even rate.
- Tax Considerations: The tax implications of your income, deductions, credits, and tax-filing status impact your break-even rate by affecting your after-tax income and disposable cash flow.
- Income Sources: The diversity and stability of your income sources, such as salaries, wages, bonuses, commissions, rental income, investment income, and side hustles, affect your break-even rate by determining your total earnings.
- Career Advancement: Opportunities for career growth, promotions, salary increases, job changes, and entrepreneurial endeavors can influence your break-even rate by altering your income potential.
- Economic Conditions: The prevailing economic conditions, such as inflation, interest rates, job market trends, and industry dynamics, may impact your break-even rate by affecting your earning capacity and purchasing power.
- Financial Planning: Your financial planning strategies, including budgeting, saving, investing, debt management, risk mitigation, and retirement planning, can shape your break-even rate by optimizing your financial resources and mitigating financial risks.
A Real-Life Example
You might be wondering how you might use this in real-life. Well, as the author of this blog and creator of this calculator, let me provide you an example from my recent experience as a SAP Project Manager. You see, even though this is a relatively high-paying type job, I get dozens of calls of a day from mostly overseas recruiters who need a SAP Project Manager. Invariably, the rate they offer is far below my asking rate, which is based on my personal break-even rate. On one of these recent ‘hot opportunities’, for which the recruiter said I was a perfect fit (keep in mind, these overseas recruiters are nothing more than people hired to work a list and have no knowledge whatsoever of what the SAP Project Manager job actually requires other than what someone wrote down for them – they are just dialing for dollars). When he made his typically laughbably low-ball offer, I managed to get him on the phone and do a walk-through of my rate using my numbers and this calculator. He could understand immediately why 150 an hour plus expenses was the lowest number, and why his number was unrealistic, if not insulting. So we finally got through him, to the client, who of course, had no idea why the recruiter was offering his low-ball offer, when the client was paying about 285 an hour! A little information clarity goes a long way to improving your lot in life.
Tips for Calculating Break-Even Rate
Calculating your break-even rate requires careful consideration of various financial factors to ensure accuracy and relevance to your personal situation. Here are some helpful tips to guide you through the process:
- Gather Financial Information: Collect detailed information about your monthly expenses, debt obligations, income sources, and savings goals to provide a comprehensive overview of your financial landscape.
- Identify Fixed and Variable Expenses: Distinguish between fixed expenses (e.g., rent, insurance premiums) and variable expenses (e.g., groceries, entertainment) to understand your essential financial commitments and discretionary spending habits.
- Estimate Monthly Income: Determine your average monthly income from all sources, including salaries, wages, bonuses, commissions, rental income, investments, and side hustles, to ascertain your total earnings potential.
- Calculate Total Expenses: Summarize your monthly expenses, including housing costs, utilities, transportation, groceries, healthcare, debt payments, and discretionary spending, to calculate your total monthly expenditures.
- Determine Break-Even Point: Divide your total monthly expenses by the number of hours you plan to work each month to identify your break-even rate, representing the minimum hourly wage required to cover your financial obligations.
- Consider Savings and Goals: Factor in your savings objectives, such as emergency funds, retirement savings, investment goals, and other financial targets, to ensure adequate provision for future financial needs and aspirations.
- Review and Adjust Regularly: Regularly review your break-even rate in light of changing financial circumstances, income fluctuations, expense adjustments, and evolving savings goals to maintain financial stability and flexibility.
By following these tips and incorporating relevant financial considerations, you can accurately calculate your break-even rate and make informed decisions about your personal finances.
Strategies for Adjusting Break-Even Rate
Adjusting your break-even rate involves implementing strategic financial tactics to optimize your financial position and achieve your long-term objectives. Here are some effective strategies to consider:
- Increase Income Streams: Explore opportunities to diversify your income sources, such as pursuing higher-paying employment opportunities, starting a side business or freelancing, investing in dividend-paying stocks, or monetizing your skills and expertise through consulting or coaching services.
- Reduce Non-Essential Expenses: Identify areas where you can trim discretionary spending without sacrificing your quality of life, such as dining out less frequently, canceling unused subscriptions or memberships, negotiating lower utility bills, or shopping for more affordable alternatives.
- Optimize Debt Management: Prioritize debt repayment strategies, such as consolidating high-interest debts, refinancing loans for better terms, negotiating lower interest rates with creditors, or implementing a structured debt payoff plan, to minimize interest costs and accelerate debt-free goals.
- Enhance Efficiency and Productivity: Streamline your daily routines, workflows, and processes to maximize your time and energy efficiency, increase productivity levels, and achieve more in less time, whether at work or in your personal life.
- Invest in Skill Development: Invest in continuous learning and skill development initiatives to enhance your professional expertise, marketability, and earning potential, whether through formal education, online courses, vocational training, or professional certifications.
- Review and Adjust Regularly: Continuously monitor and evaluate your financial progress, adjust your break-even rate as needed in response to changing economic conditions, lifestyle preferences, career opportunities, or personal priorities, and maintain flexibility in your financial planning approach.
By implementing these proactive strategies and making thoughtful adjustments to your break-even rate, you can strengthen your financial resilience, unlock new opportunities for growth and prosperity, and achieve greater financial freedom and security in the long run.
Common misconceptions about break-even rates
Common misconceptions about break-even rates can hinder your financial decision-making and prevent you from achieving your financial goals. Here are some important misconceptions to be aware of:
- Break-Even Rate is Fixed: Contrary to popular belief, your break-even rate is not set in stone and can fluctuate over time due to changes in income, expenses, debt obligations, or economic conditions.
- Break-Even Rate Equals Living Wage: While your break-even rate represents the minimum income required to cover your expenses, it does not necessarily equate to a comfortable or sustainable living wage, as it may exclude savings, investments, or discretionary spending.
- Break-Even Rate Reflects Market Value: Your break-even rate may not accurately reflect your true market value or earning potential, as it is based on personal expenses rather than industry standards, market demand, or negotiation skills.
- Break-Even Rate Determines Success: Relying solely on your break-even rate as a measure of financial success or failure overlooks other important indicators of financial health, such as net worth, savings rate, investment performance, or overall well-being.
- Break-Even Rate Dictates Career Choices: While understanding your break-even rate can inform career decisions, it should not limit your aspirations or career options, as pursuing passion, fulfillment, or long-term growth may outweigh immediate financial considerations.
- Break-Even Rate Ignored for Non-Traditional Income: Individuals with irregular or non-traditional income sources, such as freelancers, entrepreneurs, or investors, may overlook the relevance of break-even rates, assuming their income fluctuates too unpredictably to calculate effectively.
Recognizing and dispelling these misconceptions can empower you to make more informed financial choices, adapt to changing circumstances, and pursue a balanced approach to achieving financial well-being and fulfillment.
Free Interactive Personal Break-Even Rate Calculator
Are you ready to take control of your financial future? Introducing our Personal Break-Even Calculator, a powerful tool designed by two MBA-trained experts – my brother and me – to help you navigate your financial journey with confidence and clarity. Whether you’re evaluating job offers, planning your budget, or strategizing for the future, our calculator empowers you to calculate your break-even rate effortlessly. Don’t leave your financial success to chance – unlock the insights you need to thrive. Try our Personal Break-Even Calculator now and embark on the path towards financial freedom.
Just Two Inputs is All it Takes
Use the personal break-even rate calculator to find out how much you must make to take the job.
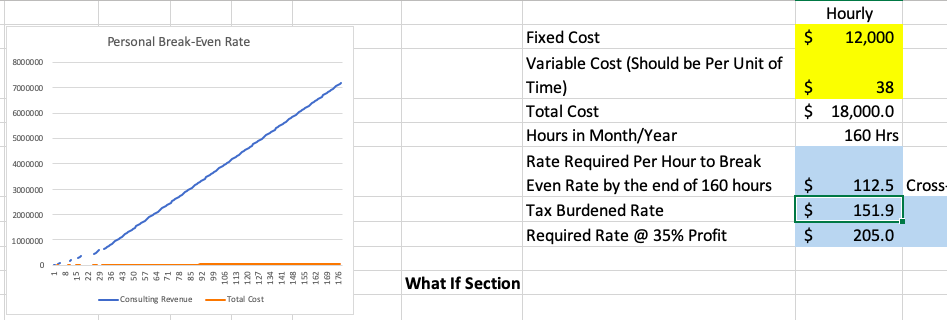
Breaking This Break-Even Rate Down
What this Personal Break-Even calculator is telling you is what hourly rate you must earn every hour you work during the month to cover all of your expenses. There are many nuggets of gold buried in this calculation. For instance, Let’s say your expenses are $1,600 a month (not likely, I know, but bear with me). That means you would only need to earn $10 an hour to cover your expenses. But what if you earn $30 bucks an hour? How many hours a month would you need to work to cover all of your expenses? Don’t you love word problems.
The math on this is simple, just divide $1,600/30=53 hours. That means you need to work 53 hours before you break-even during the month, and the remaining 107 hours can go toward savings.
Decide How Much You Want and Need To Earn
Have you wondered how much you would have to make per hour to earn a million dollars per year? Why a million? After all, how likely is it that anybody earns a million dollars a year? As it turns out, in the U.S., there are lot of people who earn that much. So let’s do the math. First off, you should know there are 2080 available work hours in a year (according to the US Government and accountants). So now you just divide $1,000,000/2080=$480.76 Per Hour.
OK, so maybe a million dollars a year is hard to wrap your mind around. Well, let’s try a more common $100,000 per year income. That works out to be $48 Per Hour.
So the next time a recruiter calls you and ask ‘what’s your rate’, you now have a tool you can answer with.